Table of Contents
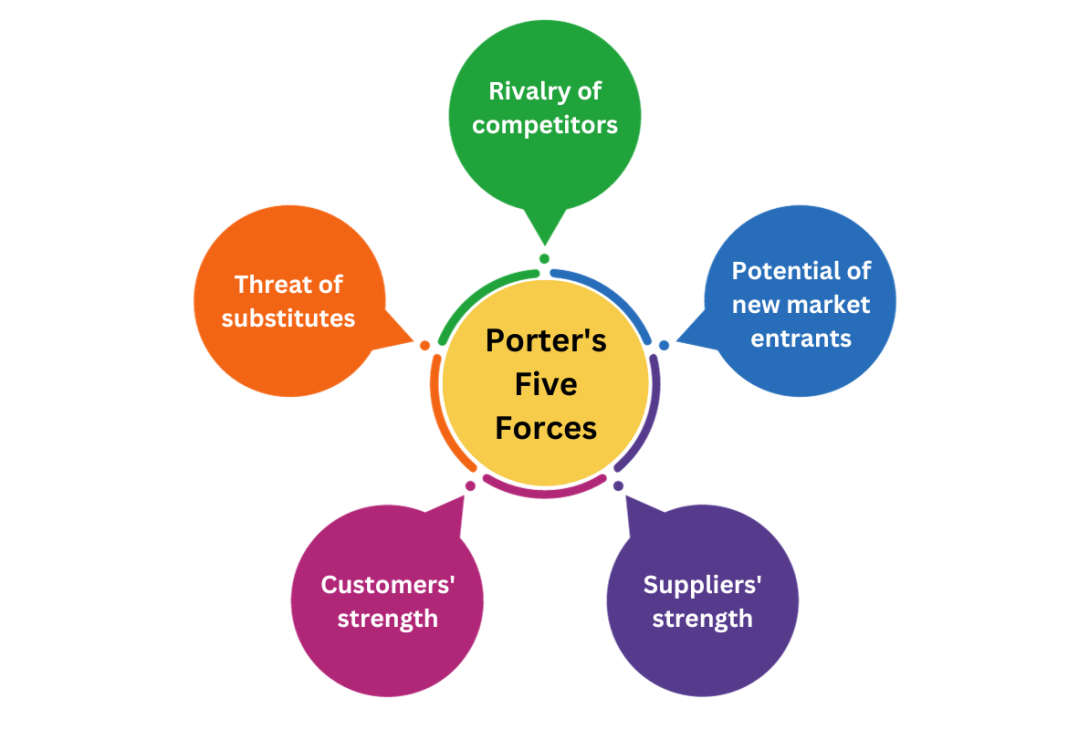
What is Porter’s 5 Forces Model?
Porter’s 5 forces model is used to analyze the competitive forces that affect the organization. Porter’s five forces model has been given the facilitation to identify and analyze the five competitive forces that are compatible with any industry, and it helps to determine the organization’s strengths and weaknesses. The study of Porter’s 5 Forces is often used to describe the structure of a market to assess corporate strategy, and it can be used to direct business strategies to improve competitive advantage.
According to Porters 5 forces model, the following are the competitive forces:
- Rivalry of Competitors
- Potential of new market entrants
- Suppliers’ strength / Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Customers’ strength / Bargaining Power of Customers
- Threat of Substitutes

1. Rivalry of Competitors
The rivalry of competitors can be identified as the first of the porters 5 forces in relation to the number of rivals and their potential to undercut a company. The greater the number of rivals, the lower the influence of a company, along with the number of comparable goods and services they sell.
Use Case: As significant competitors to the Emerald brand, Ebony Holdings, and Hameedia can be identified, and Ebony-Vantage is a leading brand that has two decades of history. Both of these rivals deliver comparable goods to consumers with little or no distinction. But with the average quality and attention to detail provided by Emerald, it is impossible for other firms to contend against them. Emerald maintains its quality rather than quantity. Quality is the prioritized factor, and they use this as the marketing strategy.

2. Potential of new market entrants
The strength of a business is also influenced by the power of fresh entrants into its market. The less time and resources it takes a rival to reach the business of a product and be a successful competitor, the more the role of an existing company will be substantially undermined.
Use Case: Emerald is leading in formals at present, and that’s their primary strength. As mentioned above, it is impossible for other businesses to compete in this sector with Emerald because of the price factor and the high quality they retain. The challenge of new entrants to the formal sector is, nevertheless, moderate.
Although there is a trend in the market for company casuals (formal linen), instead of wearing formals to work, people prefer to wear casuals. With that, Emerald looks forward to joining the casual market with a new collection under the price range of Rs. 1,000–1,200 in order to resolve this while still retaining the quality.
They have mainly acknowledged AnationZ, E-Line Apparels (a brand of EDGE), and Beverly Street (a brand of Nizhoni) as challenges to the casual market from new entrants.
Besides, many importers are flooding this market because there are no effective government policies to restrict these imports. We may also assume that the challenge to the apparel industry from new entrants is high.

3. Suppliers’ strength / Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The next element in the model of the Porter’s 5 Forces discusses how quickly suppliers can push up supply costs. It is influenced by the number of a product or service’s primary supply suppliers, how special these inputs are, and how much it would cost a business to turn to another supplier. The fewer suppliers to industry, the greater the market’s reliance on a supplier.
As a result, the producer has more strength and can raise up the cost of input and press for other trade benefits. On the other hand, a business can keep its production costs lower and increase its profits because there are multiple suppliers or low swapping costs between competing suppliers.
Use Case: Emerald has its own production facilities built in Sri Lanka, but in order to sustain the above-average standard of their goods, they import fabrics from around the world.
Significant amounts of fabric are purchased by Emerald, primarily from Japan and India. From Hokkoh Co. Ltd., Co. & Ikegami. Emerald’s big vendors are Ltd. in Japan and Rayn Cloth Factories in India.
For more than 30 years, Emerald has been working with these vendors. For this cause, these manufacturers are not prepared to risk the ability to supply such a trustworthy and reliable distributor. Therefore, suppliers’ bargaining power is low.

4. Customers’ strength / Bargaining Power of Customers
One of the Porter’s 5 Forces is the capacity of clients to push costs lower, or their level of control. It is determined by how many customers or clients a business has, how important each client is, and how much it will cost a business to pursue new clients or markets for its production.
A smaller and stronger base of consumers means that each customer has the leverage to fight for cheaper rates and better offers. In order to maximize profits, a corporation that has more or fewer individual clients would have an easier time charging higher rates. Products are sold on MRP, especially in the garment industry (maximum retail price). Therefore, they typically can’t negotiate pricing while buyers are buying something.
Use Case: Saying that, Emerald only has six shops of her own. They have 400 dealers (Nolimit, Thilakawardana, Opal, Fashion Bug, etc.) without it, with the exception of Odel and Hameedia.
Therefore, they contract with the middleman for 90 percent. So, their customers are the dealers or the middleman. The selection of goods they want is negotiated by these distributors (plain colors, stripes, dots). The business explores with the development staff and crafts its industry conditions according to such ratios with certain input.
5. Threat of Substitutes
Substitutes are the subject of the last of the poters five forces. Substitute goods or services that may be used instead of the products or services of a business pose a hazard. Companies manufacturing goods or services that do not have similar alternatives would have the leverage to lift rates and lock in attractive terms.
Customers would have the option to forgo the purchasing of a company’s goods if close alternatives are available, and the control of a company will be diminished. When it comes to clothing, clients have multiple choices to pick from. There are alternatives that can make high-end models affordable at cheaper costs, even for those who cannot afford premium brands.
Use Case: The Coco Club Brand- Beverly Street and Man United (MUN) brand- Cool World are some replacements that Emerald has known. Although the advantage that Emerald has is the prestige, they have earned for delivering premium products, where the Emerald brand has flourished in the industry.
Conclusion
Considering Porter’s 5 Forces and how they apply to an industry can allow businesses to adapt its business strategy to make better use of its resources to generate higher profits for its investor.